What Is the Economic Importance of Peanuts in the USA?
April 14, 2025 | by samayyashafique8@gmail.com
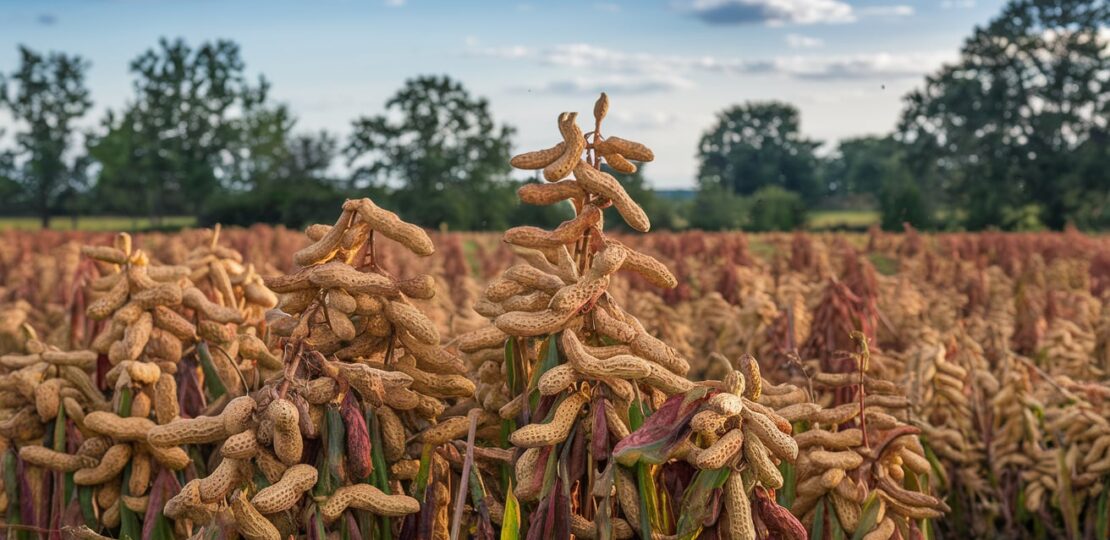

Peanuts may seem like a simple snack, but their role in the economy—especially in the United States—is anything but small. What is the economic importance of peanuts? The answer lies in their impact on agriculture, food production, trade, and industrial uses. From being a profitable cash crop for farmers to fueling a multi-billion-dollar peanut butter industry, peanuts contribute to job creation, nutrition, and sustainability.
In this article, we’ll explore how this humble legume supports the U.S. economy and why it remains a crop of global significance.
The Role of Peanuts in U.S. Agriculture
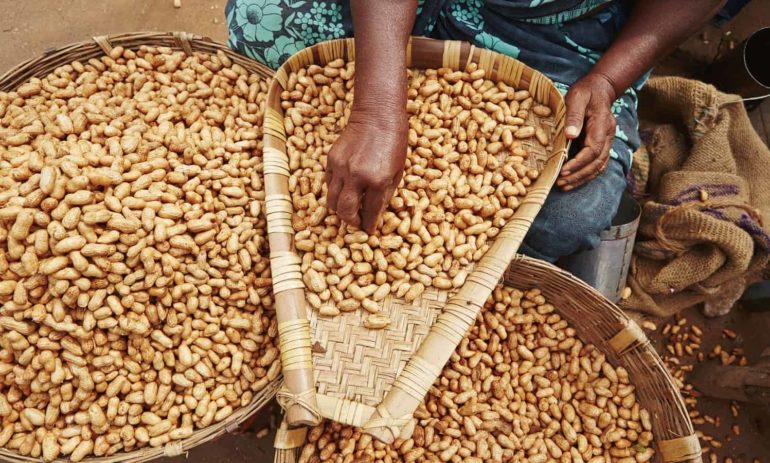

Crop Production and Farmer Income
Peanuts are one of the most important legume crops grown in the United States, particularly in southern states such as Georgia, Alabama, Texas, and Florida. These states account for the majority of the nation’s peanut production. For many farmers, peanuts represent a dependable and profitable crop that supports their livelihood.
- Georgia alone accounts for over 50% of U.S. peanut production.
- According to the USDA, peanut farmers in the U.S. generate over $1 billion in farm-level revenue annually.
Contribution to Food Security
Peanuts are an affordable and nutrient-rich food. They’re packed with:
- Protein
- Healthy fats
- Fiber
- Essential vitamins and minerals like Vitamin E, niacin, and magnesium
Because of their nutritional density, peanuts play a vital role in food assistance programs, school lunches, and emergency food supplies—enhancing national food security.
Economic Impact of the Peanut Butter Industry
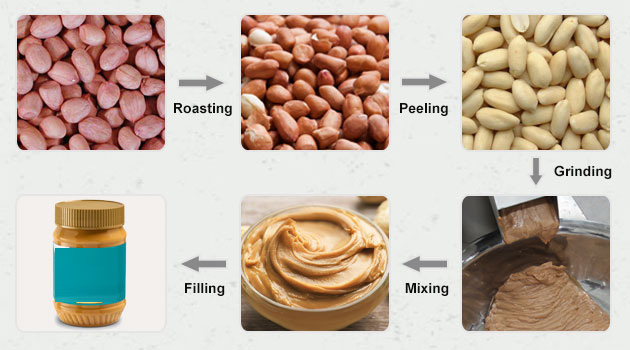
Peanut butter is not just a childhood favorite—it’s big business in the USA.
Market Size and Employment
The peanut butter industry in the U.S. is valued at over $2 billion, and it’s growing every year. This industry supports:
- Smallholder peanut farmers
- Processing plant workers
- Marketing and logistics professionals
Brands like Jif, Skippy, and Smucker’s source millions of pounds of peanuts annually, making peanut butter one of the most recognizable and consumed spreads in the country.
Domestic and Export Demand
American consumers eat over 7 pounds of peanuts per person each year, mostly in the form of peanut butter. In addition, peanut butter and peanut-based snacks are exported to countries across the globe, contributing to the positive U.S. trade balance.
Industrial and Non-Food Applications of Peanuts
Beyond food, peanuts and their byproducts offer a range of industrial uses.
Peanut Oil Production
Peanut oil is a valuable product in both domestic and international markets. It’s used for:
- High-temperature cooking
- Skincare and cosmetic products
- Biodiesel fuel production
Peanut Meal for Animal Feed
Once the oil is extracted from peanuts, what remains is a protein-rich substance called peanut meal. This is used in feed for:
- Cattle
- Pigs
- Poultry
Its high protein content and affordability make it an attractive feed option for livestock producers.
Industrial Byproducts
Peanut components have also found use in:
- Paints
- Varnishes
- Lubricants
- Adhesives
This adds further value to the peanut crop beyond traditional uses.
Peanuts and Global Trade
Peanut Exports
The U.S. is one of the world’s top peanut exporters, alongside countries like India, China, and Argentina. American peanuts are shipped to over 70 countries. In 2022, peanut exports brought in more than $600 million for the U.S. economy.
Top export destinations include:
- Canada
- Mexico
- Japan
- Netherlands
Trade Balance and Global Competitiveness
Peanuts help improve the agricultural trade balance of the United States. Thanks to their quality and safety standards, U.S. peanuts often command premium prices in international markets.
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits

Soil Health and Crop Rotation
Peanuts are legumes, which means they naturally fix nitrogen in the soil—reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. Farmers often rotate peanuts with other crops like cotton or corn to improve overall soil health and boost yields.
Water Efficiency
Compared to many other crops, peanuts are relatively drought-tolerant. They require less irrigation, making them suitable for areas where water resources are limited.
Sustainable Practices
The peanut industry has made strides in sustainability by promoting:
- Low-input farming
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Conservation tillage practices
Rural Economic Development
Job Creation in Small Communities
Peanut farming supports tens of thousands of jobs, from planting to harvesting, processing, and distribution. For many rural areas in the South, the peanut industry is a lifeline for economic activity.
Infrastructure and Growth
As demand for peanuts and their products grows, so does investment in infrastructure such as:
- Storage facilities
- Processing plants
- Transportation networks
This not only benefits the peanut sector but also improves logistics and connectivity for other industries as well.
Peanut Research and Innovation
Research into peanut genetics, pest resistance, and drought tolerance has helped boost yields and cut costs for farmers. Organizations like the National Peanut Board and USDA-ARS invest heavily in peanut R&D, ensuring the crop remains economically viable for generations to come.
Table: Peanut Uses and Their Economic Contributions
| Use Case | Economic Impact |
| Peanut Butter | $2B+ industry, job creation |
| Peanut Oil | Cooking, cosmetics, biodiesel |
| Peanut Meal | Animal feed for livestock |
| Direct Consumption | Affordable protein source |
| Industrial Uses | Paints, varnishes, lubricants |
| Export Trade | $600M+ annual exports |
Chart Suggestion: “Peanut Production by U.S. State”
Include a bar chart showing the top peanut-producing states (e.g., Georgia, Texas, Alabama, Florida, North Carolina).
What is the economic use of peanuts?
Peanuts have a wide range of economic uses. They generate income for farmers, support the food and snack industries, and are processed into valuable products like peanut butter and peanut oil. Additionally, peanut byproducts such as peanut meal are used in livestock feed, contributing to animal agriculture. Peanuts also play a role in global trade and rural economic development.
What is the commercial importance of peanuts?

The commercial importance of peanuts lies in their versatility and market demand. Peanuts are a high-value commodity used in various products, including food (e.g., roasted peanuts, peanut butter), cosmetics (e.g., peanut oil in lotions), and industry (e.g., lubricants, biodiesel). Their profitability supports a large commercial supply chain from farming and processing to marketing and export.
Why are peanuts so important?
Peanuts are important for several reasons:
- Nutritional value: Rich in protein, healthy fats, and essential nutrients
- Economic impact: A major cash crop supporting millions of jobs
- Environmental benefits: Improve soil health and require less water
- Global significance: Used in food aid and traded internationally
They contribute to food security, health, employment, and sustainability.
What are the uses of peanuts in industry?
In industry, peanuts are used in several ways:
- Peanut oil is used in cooking, cosmetics, and biodiesel
- Peanut meal is used as protein-rich animal feed
- Peanut derivatives are found in paints, varnishes, lubricants, and adhesives
These uses add significant economic value beyond peanuts’ role as a food source.
FAQs
What is the economic importance of peanuts?
Peanuts contribute to agriculture, industry, and trade by generating income for farmers, supporting food security, and powering the peanut butter and oil industries.
How do peanuts benefit farmers economically?
Peanuts provide a high-yield, profitable crop for farmers and are often used in crop rotation to enhance soil quality, reducing farming costs.
What are the industrial uses of peanuts?
Peanuts are used to produce oil, peanut meal for livestock feed, and even industrial products like paint, lubricants, and adhesives.
Closing Thoughts
So, what is the economic importance of peanuts? From fueling the American food industry to boosting rural economies and contributing to international trade, peanuts are a small crop with a massive footprint.
Their versatility, affordability, and sustainability make them a true powerhouse in the world of agriculture. Whether you’re enjoying a spoonful of peanut butter or investing in agricultural futures, you’re part of an economy that peanuts help keep thriving.
READ MORE:
RELATED POSTS
View all


